In this digital landscape, most people use instant messaging apps to connect with peers. However, SMS texting still exists owing to its 98% open-rates and compatibility with all mobile phones. Unluckily, scammers often exploit this technology to send fake login links, prize alerts, and phishing codes — putting children and teens at risk. In this guide, we’ll discuss in detail: what is SMS text, including its origin and working. We’ll also share with you effective tips to protect your kids from unsafe messages.
What is SMS text?
SMS (Short Message Service) is one of the oldest messaging services enabling users to exchange text messages between mobile devices. Each SMS is usually limited to 160 characters, including spaces or punctuation. This helps users to keep the communication quick, even when the network signals are weak.
The origin and purpose of SMS
The SMS text messaging concept was first introduced in 1982 by the two engineers Friedhelm Hillebrand & Bernard Ghillebaert. At that time, they were actually working on the early development of GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) standards. However, the main purpose of creating this technology was to ease communication even with low-bandwidth networks.
What’s more interesting is that the SMS service became active in 1992. This time, a British engineer, Neil Papworth, first sent the Merry Christmas message. However, it gained immense popularity in the early 2000s, allowing person-to-person communication and expanding to businesses or organizations.
Nowadays, even though apps like WhatsApp, Messenger, and iMessage exist, SMS, for being quick & reliable, would remain a global trend. That’s why you still receive verifications, alerts, banking codes, and simple communication via SMS.
How does SMS text messaging work?
SMS text messaging usually works operated vu cellular networks, the same as allowing voice calls. Here is a breakdown of how this SMS texting service works!
First of all, you’ll open your text messaging app. Then type the message (up to 160 characters) and enter the recipient’s phone number.
Role of SMSC: As soon as you click the send button, it doesn’t go directly to the person to whom you are messaging. Instead, it first goes through the server named Short Message Service Center (SMSC). This system indeed forwards SMS to the intended recipient.
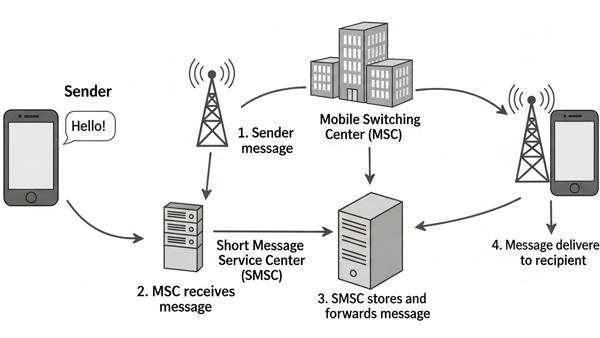


Now, suppose the recipient’s device is unavailable (switched off, out of coverage). There is no need to worry, your message doesn’t go anywhere. The SMSC temporarily stores it and waits for phone activations. Once it becomes reachable, it delivers the message, and the recipient gets notified on their mobile phone.
It’s worth noting that SMS uses the GSM 7-bit character set for encoding, which gives it a 160-character limit per message. However, when you use emojis or non-ASCII chat characters like Japanese, Arabic, or Ukrainian, this limit drops to 70 characters. This happens because such characters basically use the Unicode (UTF-16) encoding, having a character limit of up to 70/SMS.
SMS delivery vs. instant messaging delivery
| SMS Delivery | Instant Messaging Delivery | |
| Network Requirement | Cellular (no internet needed) | Internet required |
| Delivery Process | Stored & forwarded by SMSC | Sent through app servers |
| Works When Offline? | Yes | No |
| Speed | Fast but can be delayed in congestion | Usually instant with good internet |
| Compatibility | Works on all phones | Only smartphones with the app |
| Message Limits | 160 chars (70 with Unicode) | No strict limits |
| Media Support | Limited (MMS needed) | Full multimedia support |
| Reliability | Very reliable even in a weak signal | Depends on the internet quality |
Common uses of SMS texting
In the era of instant messaging apps, there are almost 4.2 billion people who actively use SMS worldwide. Let’s see its common uses for a better understanding of its huge popularity!
Personal communication: Allows you to send short updates to your friends or family members without needing a phone call or internet connection.
Business/marketing SMS notifications: Likewise, many companies also benefit from SMS to send promotions, order updates, alerts, reminders, and important notifications. This is because it has an almost 98% rate as compared to the emails, which may get lost in spam folders.
Two-factor authentication (OTP messages): Most of the legitimate platforms use the SMs service to send their users OTP messages to confirm their identity. These platforms basically do this to provide an extra security layer to your accounts, preventing any unauthorized access.
Emergency alerts & security codes: Furthermore, Governments and organizations often rely on SMS services for delivering urgent messages. Like whether its any weather warnings, or security notifications from banks, you’ll get an SMS on your mobile device.
Protect your children from online dangers lurking in SMS texts with comprehensive tracking.
Advantages and disadvantages of SMS
Although SMS is one of the classic messaging services, it plays an important role in our everyday communication. Just like other technologies, it also comes with its own strengths and weaknesses. Let’s weigh them down for better understanding!
- Works without internet: One of the most highlighted benefits of using SMS technology is that it doesn’t require any wifi or internet. You’ll just need the cellular signals to exchange messages. This makes it a straightforward way to connect with people, even in remote areas or internet outages.
- High delivery reliability: As discussed earlier, SMS usually uses an SMSC server within mobile networks that owns the task of consistent messaging delivery. This makes it ideal for important messages like OTPs and banking alerts.
- Supports all phones: In addition, SMS works on almost all devices, from classic Nokia to modern smartphones. This universal compatibility makes sure that official messages get delivered to everyone regardless of their device or internet access.
- Limited features and character range: Using the SMS service has the drawback that you can only type 160 characters per message. This way of sending detailed information requires sending multiple messages, increasing the cost. It also lacks rich features like image sharing, voice notes, or group chats unless you use MMS.
- Cost per text depends on the plan: Compared to the messaging apps that use the free internet, SMS often comes with a cost per message. This way, if you send many messages especially internationally, it would be too expensive to bear.
- Privacy risk: On top of that, standard SMS messages aren’t end-to-end encrypted. This way carries the risk of being intercepted by hackers or network providers.
What is SMS spam and phishing?
SMS, because of its high open rates, is not only used by the government or organizations; scammers also benefit from trapping people. Below are some examples helping you to understand how fraudsters use SMS to carry out scams!
Fake login links: These messages feel like they come from legitimate services like banks, having a link asking you to “verify your account”. When you click the link, it directs you to fake websites and steals your login credentials, passwords, etc.
Prize alerts: Prize alert scams usually claim that you have won the lottery, or a gift card, etc. At the same time, they mention that to claim your prize, you have to click the link or call this phone number. If you follow the instructions, scammers may try to trick you into paying a fake fee or providing personal information.
Phishing codes: These types of smishing scams are the most dangerous ones targeting to hack the data of your official accounts. For instance, scammers may text you and ask you to share your OTP to verify your access. Once you share it, they’ll immediately access your accounts.
Risks for children & teens
In this digital era, every parent brings their kids’ phones, whether to get in contact or to help with education. However, kids or teens often lack awareness about how to identify scam texts. Thereby, they are more likely to trust misleading messages and fall victim to identity theft or exposure to inappropriate content.
A report from the UK Safer Internet Centre found that nearly half (46 %) of children aged 8–17 reported being scammed. It makes it clear that youngsters are often targets of digital scams, including those sent via SMS.
Tips for protecting kids from unsafe text messages
Nowadays, with the advent of AI, scammers are becoming more sophisticated. It means identifying whether the message is real or fake is really difficult. This is worrying enough when the recipient is an adult, but when it’s a child, infinitely more so.
However, just watching kids fall victim to scams isn’t okay, as sometimes it may lead to serious consequences. Being a parent, you have to be proactive. To help you in this regard, we have come up with some effective tips that would really help you a lot in reducing risks from unsafe text messages.
Teach them not to reply to unknown numbers:
Make your kids one thing very clear: Never trust or respond to unknown messages, even if the text seems friendly. Explain to them that there may be a scammer behind, aiming to steal your sensitive information.
Do not click links or provide personal data via SMS:
Tell your kids never to click on any unknown link received via text. Guide them that there is no legitimate organization that asks its members to share their personal information or OTP via texting. Tell you, kids, that these are basically scammers tricking people into revealing sensitive data.
Block & report suspicious senders:
Besides this, you have to show your child that if they receive spam messages, they can restrict them. Like they’ll just click the number and select a block or report button. This helps prevent repeated contact from scammers and reduces exposure to unsafe messages.
Encourage open communication and educate about SMs scams:
Spend time with your kids and openly talk to them about spreading SMS scams. Keep in mind that awareness is the first line of defense; if they know what to watch out for, they are less likely to fall victim.
Unfortunately, study shows that the majority of children (72%) around the world have grappled with at least one cyber threat. Even more alarmingly, only 39 % of parents said their children had told them about such concerns. This highlights the importance of making your children feel comfortable and trusting you so they see you as someone they can freely share their concerns with.
Use of parental control apps:
Although the above-mentioned tips might prove effective. For complete peace of mind regarding kids’ safety, it’s best to leverage parental control apps like FlashGet Kids. This app combines highly advanced features to keep parents 24/7 updated about their digital whereabouts.



- Screen mirroring: See in real-time what type of messaging apps your kids are using and to whom they are chatting.
- Alerts for suspicious keywords: Allows you to set specific keywords, and instantly alerts when kids send or receive messages containing such words. This instant awareness helps you keep your kids safe from becoming prey to scams.
- SMS message monitoring: Activating the SMS safety feature lets parents check the messages sent or received on the device via the notice page.
- Usage reports: You’ll get a detailed summary of your kid’s mobile device usage on a daily basis. For instance, you can check which types of apps your kids have used and for how long.
Conclusion
In summary, the SMS texting service, owing to its quick/reliable nature, would always remain an essential communication tool worldwide. However, due to the prevalence of phishing SMS scams, staying cautious is really crucial. It’s especially important for children and teens, who are more vulnerable to fraud. By educating your kids and combining FlashGet Kids parental control tools, you would ensure your kids’ safety from potential online dangers.

